Feline
Spaying, neutering, fixing
Female cats.
Any female cat that is not being used for breeding purposes should be spayed. This procedure prevents unwanted litters and deters certain possible medical problems. Typically, cats are spayed at the age of approximately six months, but the procedure can be performed earlier or later. Older cats undergoing this and other surgeries usually require more extensive preoperative testing to assess the risk of anesthesia. Breeding cats should be spayed after retirement.
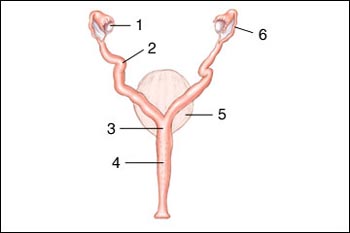
- Ovary
- Uterine Horn
- Uterine Body
- Vagina
- Bladder
- Fallopian Tube
Clinically referred to as an ovariohysterectomy, spaying involves surgically removing both the ovaries and the uterus. General anesthesia and postoperative pain management ensure that the cat will feel little to no discomfort. Although complications are possible with any surgical procedure, spaying is extremely safe, effective, and inexpensive.














